Welcome to the world of marketing, where understanding the 7 Ps is essential for success. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the fundamental components of marketing strategy and shed light on the importance of each P.
Whether you are a seasoned marketer or just starting your journey, this knowledge will empower you to create impactful marketing campaigns. So, let’s begin!
Table of Contents
The Foundation of Marketing: Exploring the 7 Ps
- Understanding the Concept of the 7 Ps of Marketing
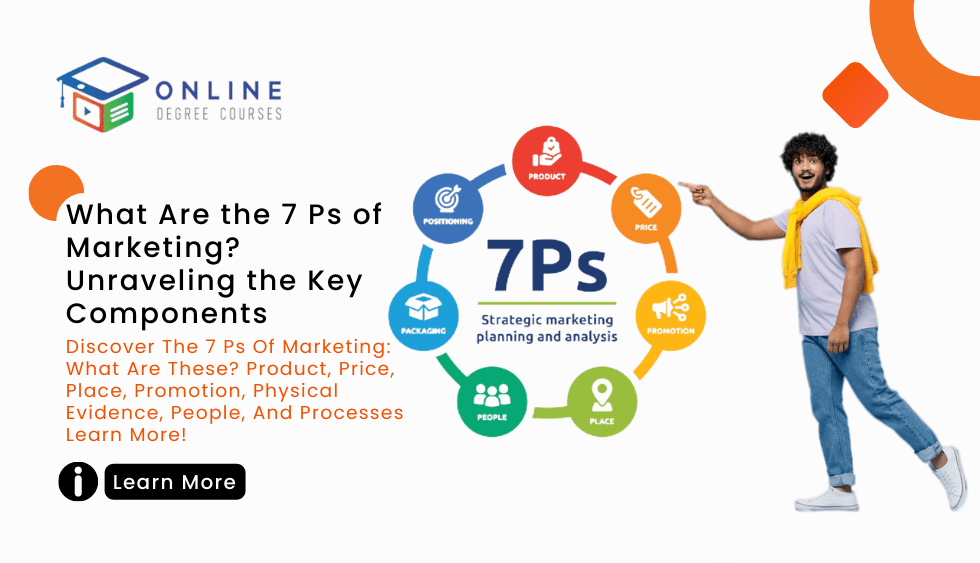
Marketing involves much more than just promoting a product or service. The concept of the 7 Ps for marketing provides a holistic framework that encompasses all aspects of a marketing strategy.
This 7 Ps for marketing are Product, Price, Place, Promotion, People, Process, and Physical Evidence. Each P represents a key element that marketers need to consider and optimize in order to achieve their objectives.
- The Evolution and Significance of the 7 Ps Framework
The 7 Ps framework was originally introduced by E. Jerome McCarthy in the 1960s and later expanded upon by Philip Kotler. This framework revolutionized the field of marketing by shifting the focus from a product-centric approach to a customer-centric one.
It emphasizes the importance of understanding the needs and preferences of target customers and aligning marketing strategies accordingly.
- Linking the 7 Ps to Marketing Strategy
Effective marketing strategies are built upon the interplay of the 7 Ps. Each P represents a crucial aspect that contributes to the overall success of a marketing campaign.
By considering these elements holistically, marketers can create a cohesive strategy that maximizes value for both the business and the customer. Let’s explore each P in detail.
1. Product: Building Blocks of Success
- Defining the Product P and Its Role in Marketing
Product (P) refers to the offering or solution that a business provides to meet customer needs. It encompasses both tangible goods and intangible services.
Understanding the target market, conducting market research, and developing a unique value proposition are essential for creating successful products that resonate with customers.
- Product Development and Differentiation Strategies
Product development involves continuous innovation and improvement to stay ahead in a competitive market.
By identifying customer pain points and addressing them through product enhancements or new product offerings, businesses can differentiate themselves from competitors and create a distinct brand identity.
- Meeting Customer Needs with Innovative Offerings
Innovation plays a vital role in product success. By anticipating and fulfilling customer needs through creative and innovative solutions, businesses can capture market share and build customer loyalty.
Continuous market research and feedback analysis are essential for identifying emerging trends and adapting product offerings accordingly.
2. Price: Balancing Value and Profitability
- The Price P: Setting the Right Value Proposition
Pricing (P) is a strategic decision that directly impacts a business’s revenue and profitability.
Setting the right price involves finding a balance between delivering value to customers and ensuring the business’s financial viability.
Factors such as production costs, competition, market demand, and perceived value all influence the pricing strategy.
- Pricing Strategies and Their Impact on Consumer Behavior
Different pricing strategies, such as penetration pricing, skimming pricing, or value-based pricing, can influence consumer behavior and perception.
Price discounts, bundling, or tiered pricing models are also commonly employed to attract and retain customers. Understanding the target market’s price sensitivity and willingness to pay is crucial for devising an effective pricing strategy.
- Competitive Pricing and Pricing Models in the Digital Age
In the digital age, pricing transparency and intense competition require businesses to stay vigilant and agile in their pricing approaches.
Dynamic pricing models, personalized pricing based on customer segments, and competitive benchmarking are strategies that can help businesses navigate the challenges of online markets and optimize their pricing decisions.
3. Place: Reaching the Right Audience
- The Place P: Distribution Channels and Market Reach
The Place (P) focuses on how businesses make their products or services available to customers.
It involves selecting appropriate distribution channels, managing logistics, and ensuring efficient supply chain operations.
Understanding the target market’s purchasing habits and preferences is vital for determining the right distribution strategy.
- Selecting Distribution Channels for Maximum Impact
Different products and target markets require specific distribution channels. Businesses must consider factors such as convenience, accessibility, cost-effectiveness, and the ability to reach the target audience.
Whether it’s direct sales, e-commerce platforms, wholesalers, or retailers, selecting the right distribution channels can significantly impact market reach and customer satisfaction.
- E-commerce and the Rise of Online Marketplaces
The digital revolution has transformed the way businesses reach customers. E-commerce platforms and online marketplaces have opened up new opportunities for businesses to expand their reach globally.
By leveraging the power of technology and online channels, businesses can tap into a vast customer base and provide a seamless shopping experience.
4. Promotion: Communicating Your Message
- The Promotion P: Crafting Effective Marketing Communications
Promotion (P) involves the strategic communication of a business’s message to its target audience. It encompasses advertising, public relations, sales promotions, and other promotional activities.
By creating compelling and targeted marketing communications, businesses can raise brand awareness, generate leads, and influence consumer perceptions.
- Integrated Marketing Communications (IMC) Strategies
Integrated Marketing Communications (IMC) is a coordinated approach that ensures all marketing communications work together synergistically.
By maintaining consistency across various channels and touchpoints, businesses can reinforce their message and enhance brand recall. IMC strategies incorporate a mix of traditional and digital marketing channels to reach customers effectively.
- Harnessing the Power of Digital Marketing Channels
In the digital era, businesses have an array of digital marketing channels at their disposal. From social media marketing and content marketing to search engine optimization and influencer collaborations.
Digital channels provide opportunities for precise targeting, real-time engagement, and data-driven optimization. Leveraging these channels effectively can result in significant brand exposure and customer engagement.
5. People: The Human Element of Marketing
- The People P: Understanding Customer Relationship Management
People (P) are at the heart of marketing, both as customers and as employees. The People P focuses on understanding customers’ needs, preferences, and behaviors.
By adopting a customer-centric approach and leveraging customer relationship management (CRM) tools such as Zendesk, MailChip, and strategies, businesses can develop strong relationships, foster loyalty, and enhance customer satisfaction.
- Creating Positive Customer Experiences
Customer experience encompasses all interactions a customer has with a business, from initial contact to post-purchase support.
By consistently delivering positive experiences that exceed customer expectations, businesses can build a loyal customer base and benefit from positive word-of-mouth referrals.
Training employees, implementing customer feedback systems, and personalizing interactions are key elements in creating memorable experiences.
- Building Strong Customer Relationships
Building strong customer relationships is essential for long-term success. By investing in relationship-building initiatives, such as loyalty programs, personalized communication, and excellent customer service, businesses can foster trust and loyalty.
Repeat customers often provide a significant portion of a business’s revenue, making customer retention a critical aspect of marketing strategy.
6. Process: Streamlining for Efficiency
- The Process P: Optimizing Marketing Operations
Process (P)Marketing processes and workflows impact the efficiency and effectiveness of marketing activities.
Streamlining processes, reducing bottlenecks, and implementing agile project management methodologies can enhance productivity and ensure the timely execution of marketing campaigns.
Regular evaluation and optimization of processes help businesses stay agile in a dynamic market environment.
- Mapping Customer Journeys and Enhancing Experiences
Understanding the customer journey is crucial for designing marketing processes that align with customers’ needs at each stage.
By mapping customer touchpoints and analyzing their experiences, businesses can identify pain points, optimize interactions, and provide relevant content or support.
This customer-centric approach enhances customer satisfaction and drives conversion.
- Implementing Marketing Automation for Efficiency
Marketing automation tools and technologies can streamline repetitive tasks, enhance marketing efficiency, and improve lead nurturing and conversion rates.
Automating email marketing, social media scheduling, lead scoring, and customer segmentation can free up valuable time for marketers to focus on strategic activities.
However, careful planning and customization are required to ensure automation aligns with customer preferences.
7. Physical Evidence: Tangible Touchpoints
- The Physical Evidence P: Enhancing Brand Perception
Physical evidence (P) refers to tangible elements that customers encounter during their interactions with a business, such as packaging, signage, retail store layout, or website design.
These touchpoints influence brand perception and play a vital role in creating a positive brand image. Consistency in design, quality, and presentation is essential to reinforce the brand’s identity.
- Designing Engaging Brand Experiences
Businesses must design physical touchpoints that create memorable experiences and differentiate themselves from competitors.
Attention to detail in product design, packaging, store ambiance, or website user experience can leave a lasting impression on customers.
By infusing creativity and aligning these touchpoints with the brand’s values, businesses can evoke positive emotions and build strong connections with customers.
- Aligning Physical and Digital Touchpoints
In an increasingly digital world, aligning physical and digital touchpoints is crucial for maintaining a consistent brand experience.
Businesses must ensure that their online presence, including websites, social media profiles, and mobile apps, reflects the same brand identity and messaging as their physical touchpoints.
Seamless integration of the physical and digital realms enhances customer engagement and brand loyalty.
Case Studies: Real-World Examples of the 7 Ps in Action
- Examining Successful Marketing Campaigns
Case studies provide valuable insights into how businesses have effectively implemented the 7 Ps to achieve marketing success.
By examining real-world examples, marketers and MBA Digital Marketer can gain inspiration and learn from strategies that have yielded positive results.
Analyzing different industries and contexts helps broaden perspectives and encourages innovative thinking.
- Analyzing How Brands Implement the 7 Ps
Successful brands excel in implementing the 7 Ps for marketing by aligning their marketing strategies with their overall business objectives.
Through case studies, marketers can analyze how brands have differentiated their products, priced them strategically, selected optimal distribution channels, and effectively promoted their offerings.
These insights can inform and shape marketing strategies across various industries.
- Lessons Learned and Takeaways for Your Marketing Strategy
By doing online degree courses in Marketing and studying successful marketing campaigns and brand implementations of the 7 Ps for marketing can provide valuable lessons and takeaways for marketers.
By distilling key principles and best practices, marketers can apply these insights to their own marketing strategies. Adaptation, innovation, and continuous learning are essential to stay competitive in the ever-evolving marketing landscape.
Final Thoughts
Congratulations! You have now unraveled the key components of the 7 Ps of marketing. By mastering these fundamental elements, you are equipped with the knowledge and insights to develop effective marketing strategies.
Remember, marketing is a dynamic field, and staying updated with the latest trends and consumer behaviors is crucial. Embrace the power of the 7 Ps and leverage them to drive business growth. So go ahead, apply this knowledge, and unleash your marketing potential.